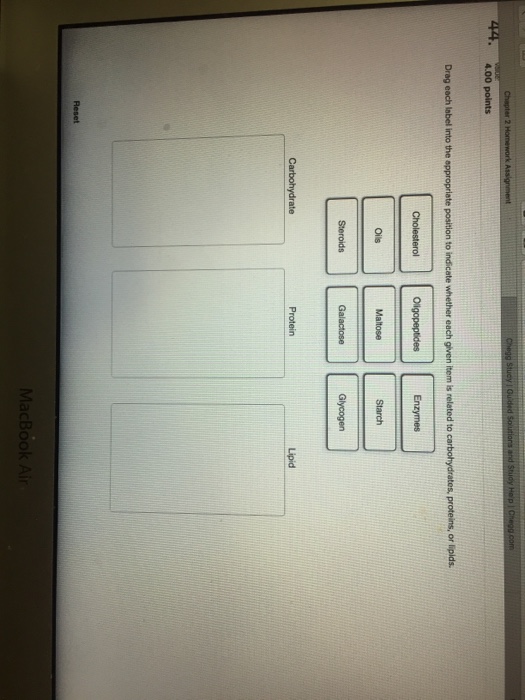
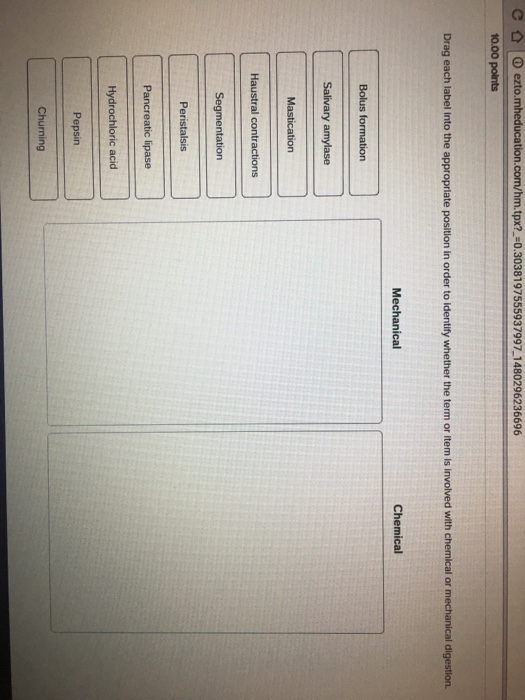
44 drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound
Label Only the Accessory Organs of the Digestive System. Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. Which are organs or accessory organs of the digestive system. The organs discussed above are the organs of the digestive tract through which food passes. BIOLOGY G - Essay Help Label five wells of the spot plate with the letters A through E. Add a few drops of each unknown solution into the appropriate well of the spot plate. Test the pH of ea… change the whale Dichotomous key to a branched/tree version Key to identify whales 1a. baleen plates Go to 2 1b. teeth Go to 4 2a. dorsal fin Go to 3 2b.
(PDF) Principles and Techiniques of Biochemistry and Molecular … Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
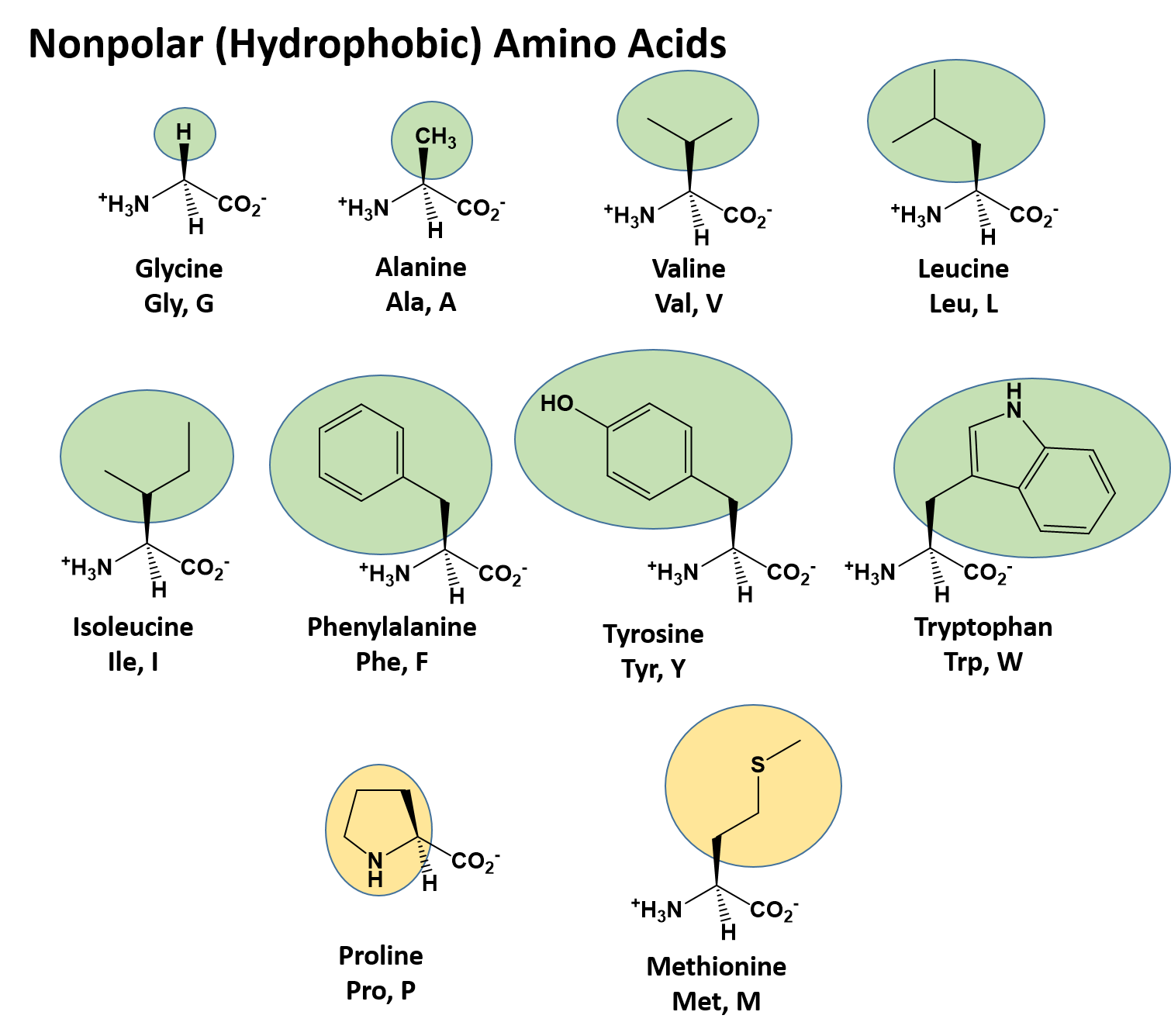
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound
Cellular organelles and their functions | Kenhub The cytoplasm is a fluid matrix that usually surrounds the nucleus and is bound by the outer membrane of the cell. Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions ... Monosaccharides - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The monosaccharide consists of single unit which contains carbon chain of three to six carbon. They can combine through glycosidic bonds to form larger carbohydrates. The main function of monosaccharide is to produce and store energy. Glucose and fructose are the most available monosaccharide in nature. Digestive Enzymes and its Types -Amylase, Protease and Lipase - BYJUS Amylase is defined as a digestive enzyme that breaks starch into small carbohydrate molecules. This enzyme is produced in two areas. Firstly, salivary glands in our mouth generate salivary amylase that starts the process of digestion by breaking down starch and converting it into maltose and smaller carbohydrate.
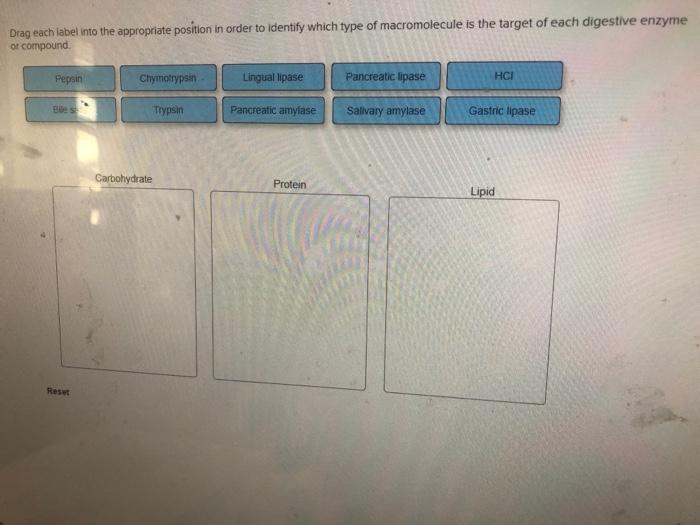
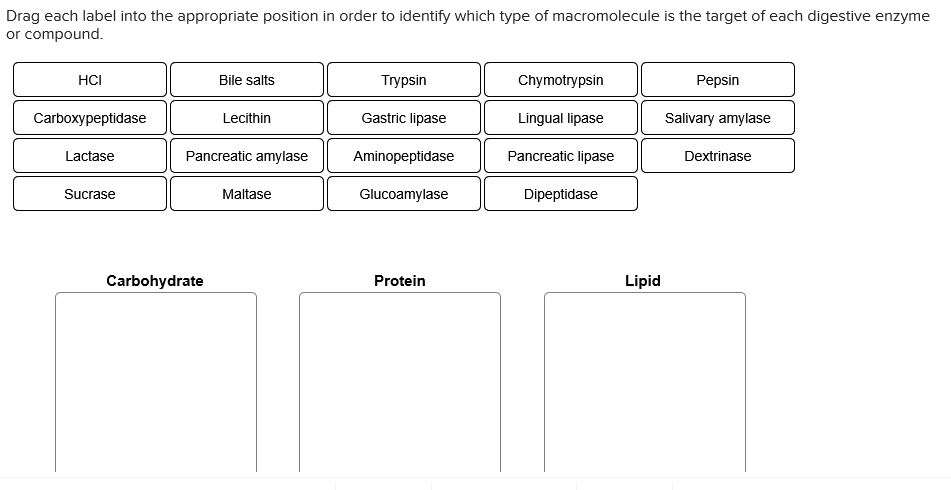
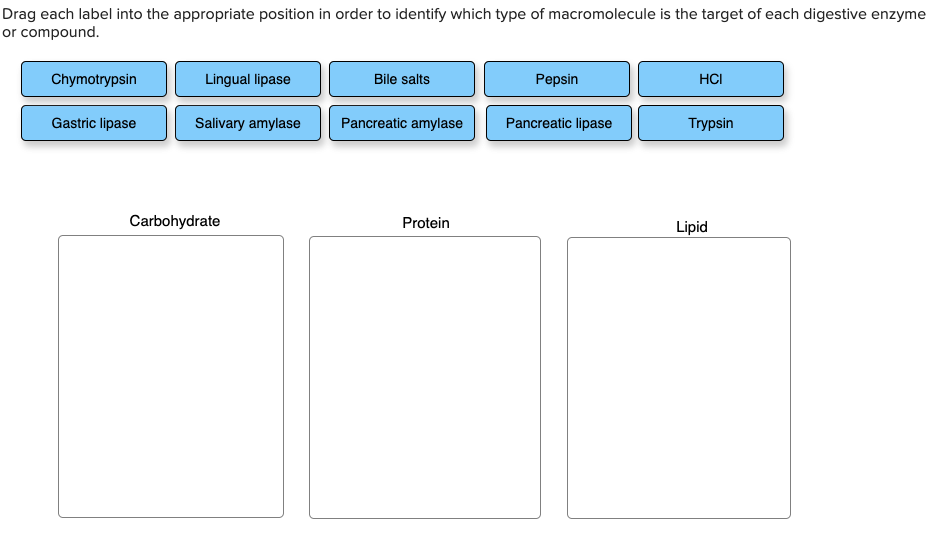
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. 9.1 The Structure of DNA - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The DNA molecule is a polymer of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogenous base, a five-carbon sugar (deoxyribose), and a phosphate group. There are four nitrogenous bases in DNA, two purines (adenine and guanine) and two pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine). A DNA molecule is composed of two strands. Contoh Karangan Bahas Terbaik Stpm Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. Which are organs or accessory organs of the digestive system. The organs discussed above are the organs of the digestive tract through which food passes. label the parts of a wave frequency - ltmwani.org A wave can make a leaf bob up and down on the water, but it cannot move the leaf magnetic waves contain electric and magnetic parts that vibrate . 10. Add your answer and earn points. . Circle the appropriate words to describe the waves at the LEFT end of this wave spectrum 7. Label it properly. Solved Drag each label into the appropriate position in - Chegg Question: Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. Chymotrypsin Lingual lipase Bile salts Pepsin HCI Gastric lipase Salivary amylase Pancreatic amylase Pancreatic lipase Trypsin Carbohydrate Protein Lipid This problem has been solved!
Transport of Oxygen in the Blood | Biology for Majors II - Lumen Learning Describe how oxygen is bound to hemoglobin and transported to body tissues. Although oxygen dissolves in blood, only a small amount of oxygen is transported this way. Only 1.5 percent of oxygen in the blood is dissolved directly into the blood itself. Most oxygen—98.5 percent—is bound to a protein called hemoglobin and carried to the tissues. CH103 - Chapter 8: The Major Macromolecules - Chemistry 11.1 Introduction: The Four Major Macromolecules Within all lifeforms on Earth, from the tiniest bacterium to the giant sperm whale, there are four major classes of organic macromolecules that are always found and are essential to life. These are the carbohydrates, lipids (or fats), proteins, and nucleic acids. Success Essays - Assisting students with assignments online Get 24⁄7 customer support help when you place a homework help service order with us. We will guide you on how to place your essay help, proofreading and editing your draft – fixing the grammar, spelling, or formatting of your paper easily and cheaply. drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify Answered step-by-step drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound: Carbohydrate, Lipid, Protein? Dipeptidase HCI bile salts Lecithin glucoamylase trypsin pancreatic amylase aminopeptidase dextrinase lactase Biology Science Anatomy
AP Biology - CourseNotes 3 reactions changing glucose into a compound that can be readily cleaved into 3-carbon phosphorylated molecules; 2 of the reactions require use of ATP; step B - cleavage/rearrangement 2 reactions break up 6-carbon molecule into 2 3-carbon molecules; 1st of 2 reactions forms G3P and another molecule that turns into G3P through the 2nd reaction Digestive Flashcards | Quizlet digestion is the breakdown large organic molecules into component parts that can be absorbed. carbohydrates are digested into (monosaccharides), protein into (amino acids), and triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol match the types of digestion with the correct description mechanical digestion- includes mastication and mixing food Substancial | PDF | United Kingdom | Spain - Scribd played war before english usually each same de area number second did being small work now could long j however group what any started way since around d both commune while important example through famous department another east west town water until sometimes game said series person named much large several place country main government century c means … BILOGY C - Essay Help 1) Choosing a Micropipettor For each of the following volumes, which micropipettor would be most appropriate to use (P1000, P200, or P20)? EX. 737 ul P1000 1. 1 pl 2. 19 pl 21 ul 4. 150 pl 400 pl C Draw a labelled diagram that explains the pressure-flow model of nutrient movement inside phloem in plants.
3 Molecular Structure and Function - NCBI Bookshelf All biological functions depend on events that occur at the molecular level. These events are directed, modulated, or detected by complex biological machines, which are themselves large molecules or clusters of molecules. Included are proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids, and complexes of them. Many areas of biological science focus on the signals detected by these machines or the ...
DOC Science Enhanced S&S Biology - Virginia Type of Macromolecule Elements (C, H, O, N, S, P) Monomer ... Have them label the parts of the cell as appropriate, showing at least the. cell wall. cytoplasm. nucleus. nuclear membrane. chromosomes. chromatin. cell plate. 2. For fresh material, have students use the procedure found in a standard reference manual, or use the method described at ...
Enzymes and the active site (article) | Khan Academy The answer depends on the enzyme. Some enzymes speed up chemical reactions by bringing two substrates together in the right orientation. Others create an environment inside the active site that's favorable to the reaction (for instance, one that's slightly acidic or non-polar).
Solved > Drag each item to the correct thermoregulatory strategy ... Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify whether the structure is an actual part of the digestive tract or an accessory... Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound....
Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify ... Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify where each secretion enters the GI tract. Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the appropriate position.Then, re-arrange the sentences into a logical order of digestive processes. Complete each sentence by dragging the proper label into the correct position.
Chapter 17 digestive Flashcards - Easy Notecards Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. 20 Indicate where each enzyme (or its inactive precursor) is produced. 21 Classify each enzyme based on the substrate it decomposes. 22 The figures depict the stages of swallowing.
Find Jobs in Germany: Job Search - Expat Guide to Germany Browse our listings to find jobs in Germany for expats, including jobs for English speakers or those in your native language.
BIO23 F19-S20 Complete Course Guide by Human Anatomy - Issuu List each type of bond in order by relative strength. b. Explain the mechanism of each type of bond. c. Provide biologically significant examples of each. ... Draw and label each of the functional ...
Solved > Drag each label into the appropriate position in:277816 ... Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound.... Drag each label into the appropriate position to identify what type of immunity is classified by each label.....this is the only one I have left...
pearsoncmg.com Labeling, ranking, sorting, or sentence completion questions. All of these question types require you to position items into an area of the answer box. Answer these kinds of questions on a computer, not on a smartphone. Press Tab to move forward or Shift/Tab to move backwards through the provided answer items.
Unit 6 Flashcards | Quizlet Drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound. Carbohydrate: Salivary amylase Pancreatic amylase Protein: Pepsin HCI Trypsin Chymotrypsin Lipid: Lingual Lipase Pancreatic lipase Gastric lipase Bile salts. During meiosis, homologous pairs of chromosomes can exchange pieces of …
Solved Drag each label into the appropriate position in - Chegg question: drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound gastric lipase pancreatic amylase lactase lecithin carboxypeptidase salivary amylase dipeptidase maltase pancreatic lipaso lingual lipase aminopeptidase sucrase dextrinase bile salts trypsin …
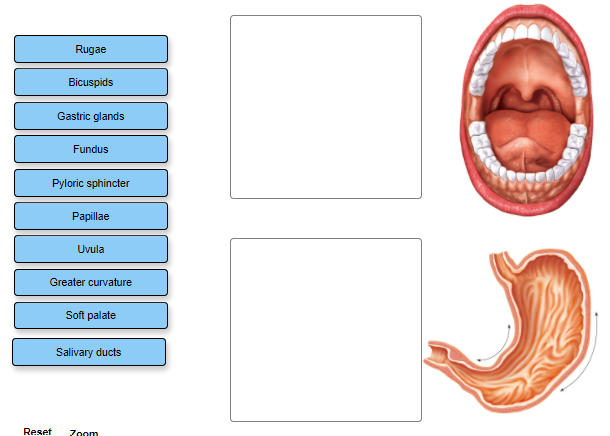
A&P Ch 17 Digestive Homework Flashcards | Quizlet The root canal of a tooth contains gingiva. blood vessels and nerves. cementum. dentin. blood vessels and nerves. Anatomy of stomach and oral cavity Identify whether the structures are associated with the oral cavity or the stomach by dragging each label into the appropriate position. Oral: Bicuspids Uvula Salivary ducts Papillae Soft palate
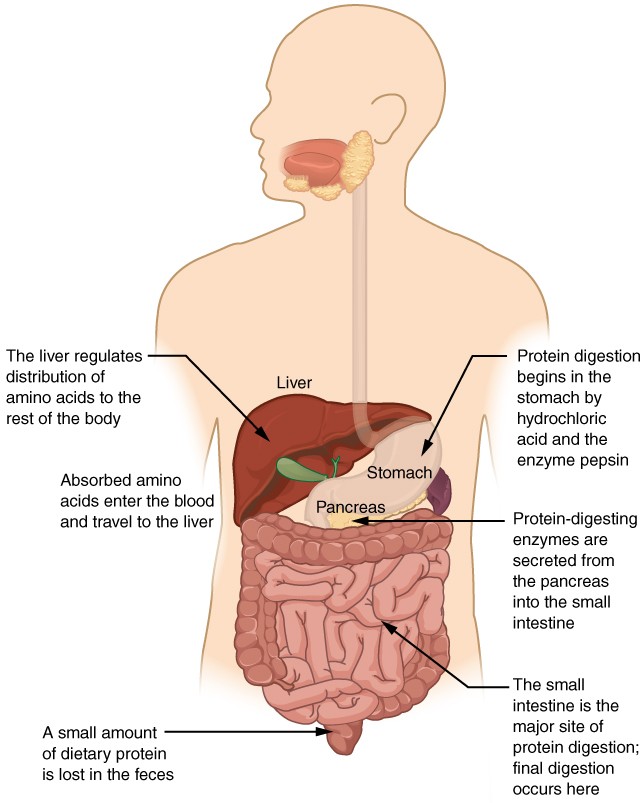
11.2 Digestive System - Concepts of Biology - 1st Canadian Edition The stomach is a saclike organ that secretes gastric digestive juices. Protein digestion is carried out by an enzyme called pepsin in the stomach chamber. The highly acidic environment kills many microorganisms in the food and, combined with the action of the enzyme pepsin, results in the catabolism of protein in the food.
Digestive Enzymes and its Types -Amylase, Protease and Lipase - BYJUS Amylase is defined as a digestive enzyme that breaks starch into small carbohydrate molecules. This enzyme is produced in two areas. Firstly, salivary glands in our mouth generate salivary amylase that starts the process of digestion by breaking down starch and converting it into maltose and smaller carbohydrate.
Monosaccharides - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics The monosaccharide consists of single unit which contains carbon chain of three to six carbon. They can combine through glycosidic bonds to form larger carbohydrates. The main function of monosaccharide is to produce and store energy. Glucose and fructose are the most available monosaccharide in nature.
Cellular organelles and their functions | Kenhub The cytoplasm is a fluid matrix that usually surrounds the nucleus and is bound by the outer membrane of the cell. Organelles are small structures within the cytoplasm that carry out functions necessary to maintain homeostasis in the cell. They are involved in many processes, for example energy production, building proteins and secretions ...







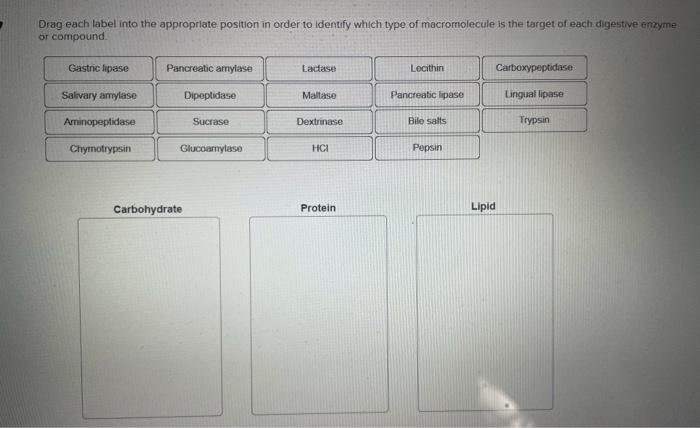



















Post a Comment for "44 drag each label into the appropriate position in order to identify which type of macromolecule is the target of each digestive enzyme or compound"