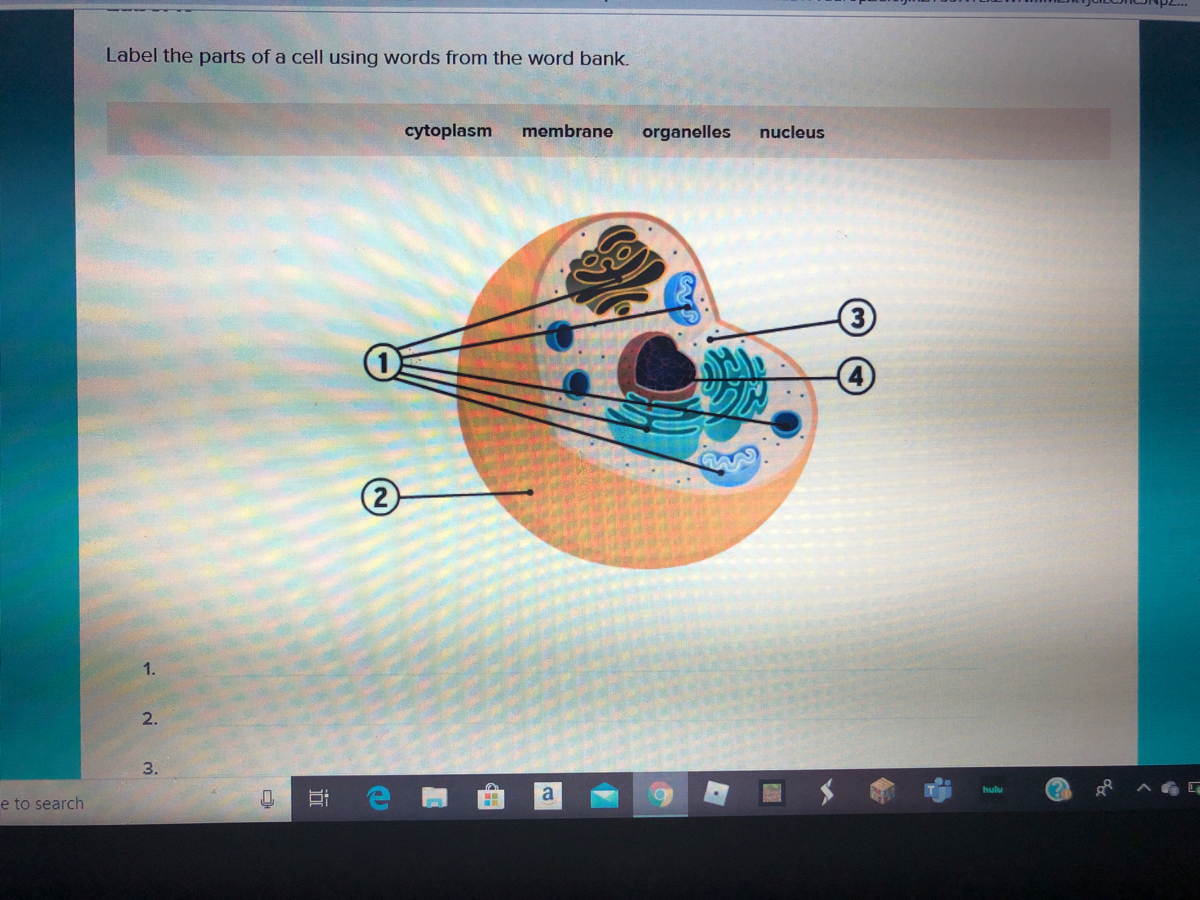
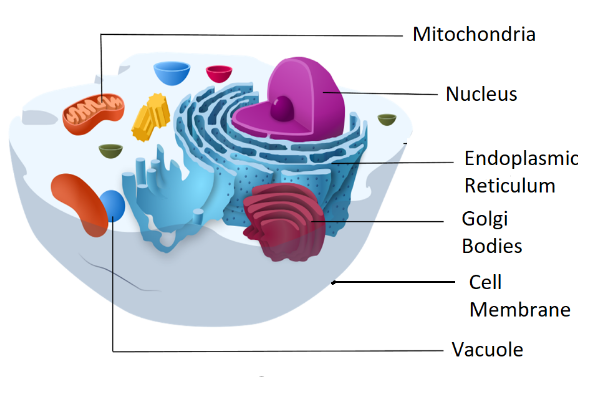
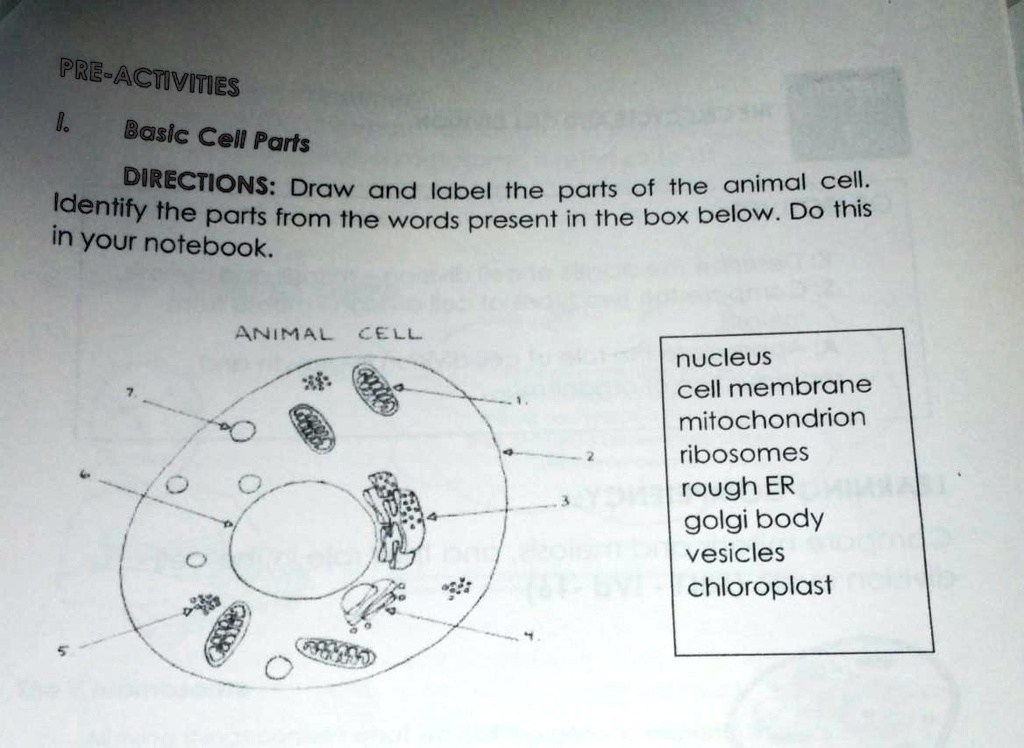
41 label the parts of the cell
Label a cell, Labeling parts of a cell, Cells Structures and Functions ... A rigid outer layer that surrounds plant cells, supports and protects the cell Location Term large central vacuoles Definition the source of water for the cell Location Term Chloroplast Definition Where photosynthesis occurs to make oxygen and glucose, only found in plant cells Location Term Ribosome Definition Makes protein Location Term Parts of a Cell Quiz | Britannica Answer: In cells with a clearly defined nucleus (called eukaryotic cells), the Golgi apparatus is the membrane-bound organelle responsible for transporting, modifying, and packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles. Question: Within a cell, what is a space that is empty of cytoplasm, lined with a membrane, and filled with fluid?
03 Label the Cell Diagram | Quizlet Control center of the cell Location Term Nucleolus Definition Ribosome synthesis Location Term Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Protein transport Location Term Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Lipid synthesis Location Term Mitochondrion Definition Cellular Respiratoin Location Term Golgi Apparatus Definition Packaging and export
Label the parts of the cell
Free Anatomy Quiz - The anatomy of the cell - Quiz 1 centrioles, the cytoplasm, the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, the golgi complex, lysosomes, microfilaments, mitochondria, the nucleolus, the nucleus, the nuclear membrane, pinocytotic vesicles, the plasma membrane, ribosomes and vacuoles. Take your knowledge of the cell further with our cell physiology quizzes : Quiz 1 --- Quiz 2 Structure of a cell | Biology library | Science | Khan Academy At the cellular level, though, some of the key differences include a cell nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, which you have (and the bacterium lacks). Here, we'll look in detail at the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Learn Cell size Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells Intro to eukaryotic cells Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy Image modified from OpenStax Biology. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group.
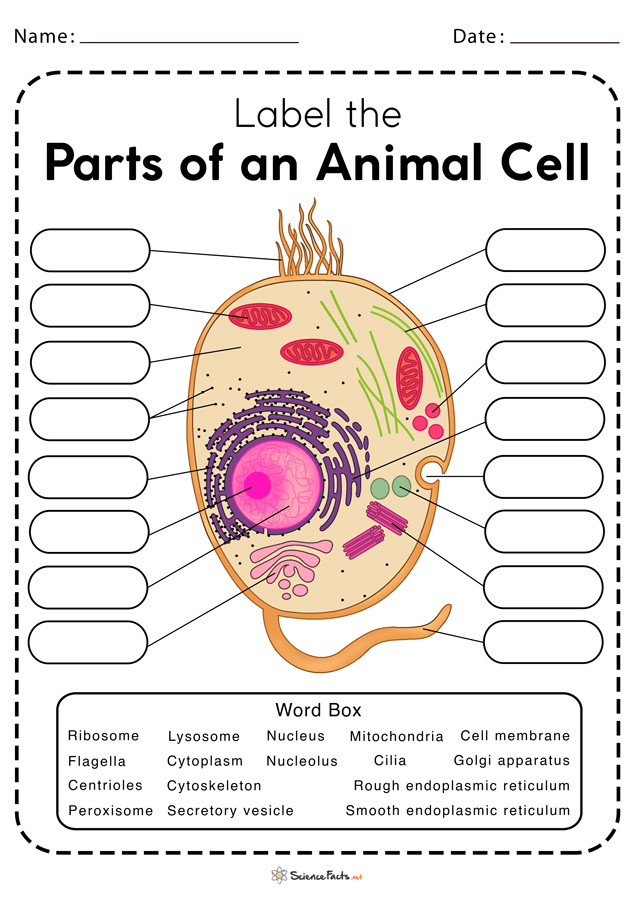
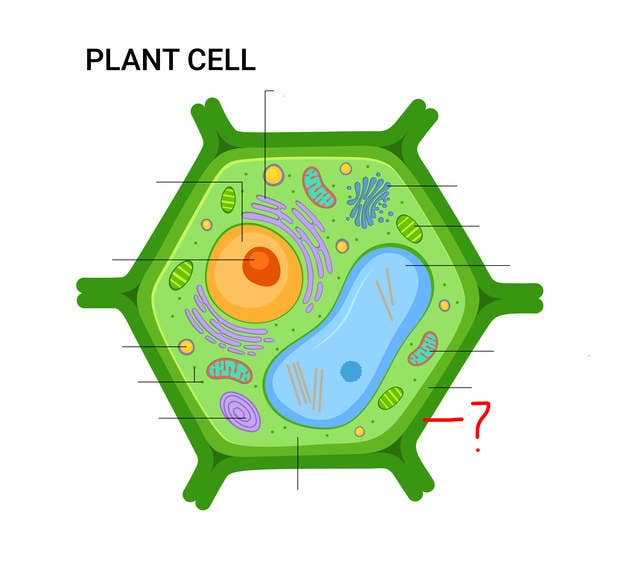
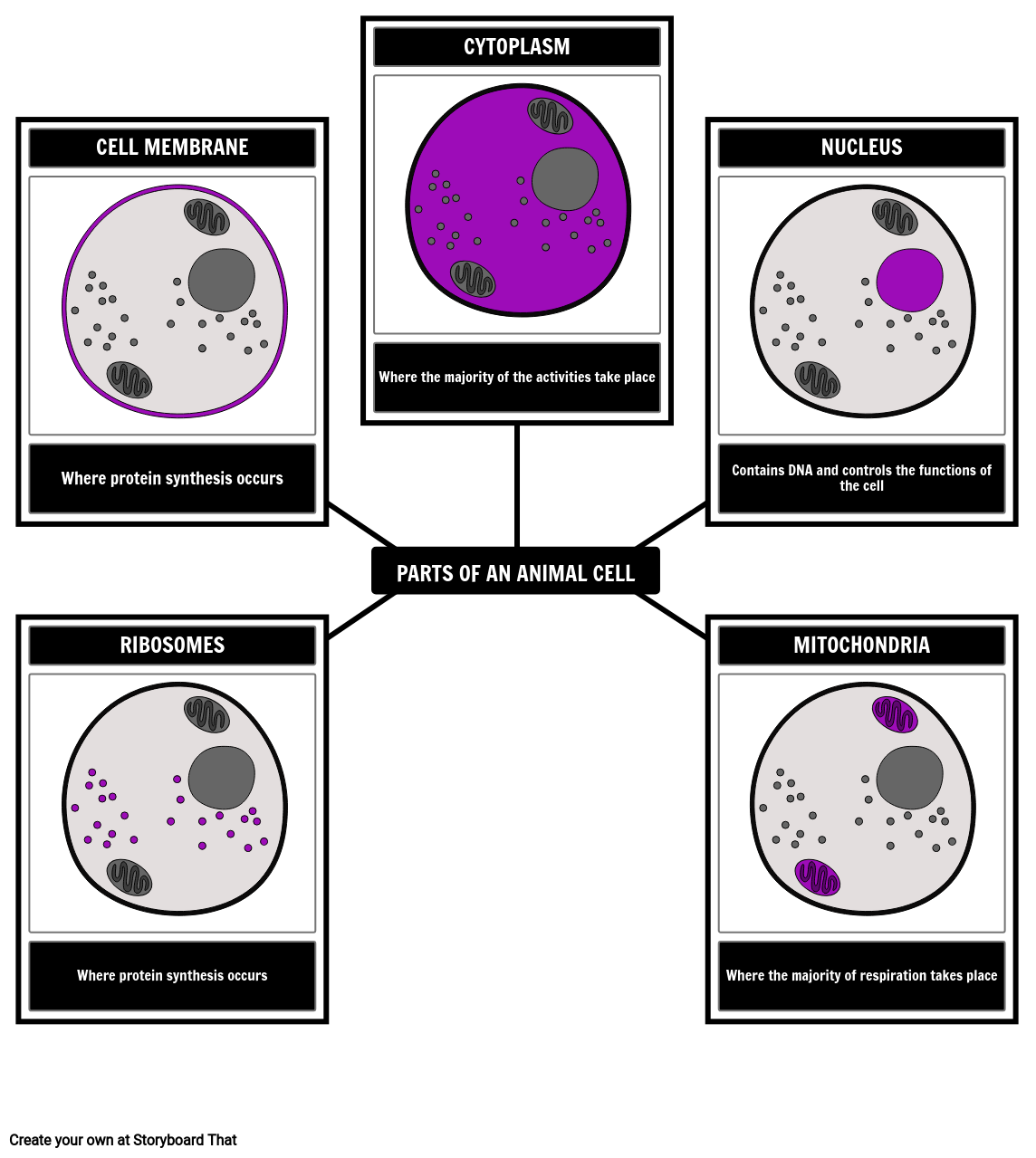
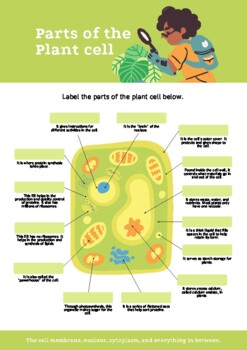
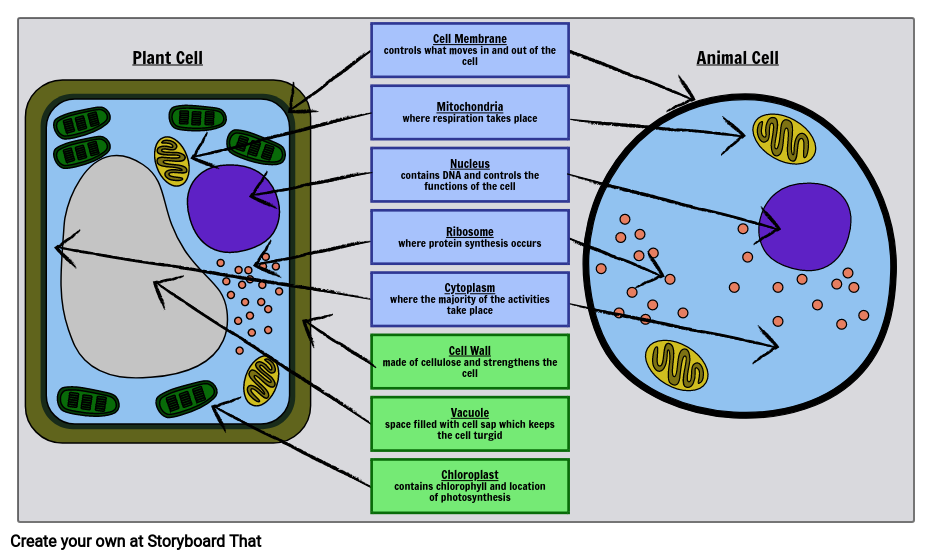
Label the parts of the cell. Learn the parts of a cell with diagrams and cell quizzes There exist two general classes of cells: Prokaryotic cells: Simple, self-sustaining cells (bacteria and archaea) Eukaryotic cells: Complex, non self-sustaining cells (found in animals, plants, algae and fungi) In this article, we'll be focusing on eukaryotic cells. Two major regions can be found in a cell. Label Cell Parts | Plant & Animal Cell Activity | StoryboardThat A correct poster of a plant cell with labels would include: cell membrane, mitochondria, nucleus, ribosome, cytoplasm, cell wall, vacuole, and chloroplast. What are the parts of an animal cell? When plant and animal cells are labeled, they have very similar parts. Labeling a Cell Diagram | Quizlet Labeling a Cell + − Flashcards Learn Test Match Created by MissEStrauss Teacher Terms in this set (15) Term Nucleus Definition The command center of the cell. It controls cell's activity. Location Term Cytoplasm Definition A jelly-like substance that fills the cell. All of the cell's organelles are located here. Location Term Vacuoles Definition Cell Parts and Functions | Biology Dictionary All cells contain specialized, subcellular structures that are adapted to keep the cell alive. Some of these structures release energy, while others produce proteins, transport substances, and control cellular activities. Collectively, these structures are called organelles.
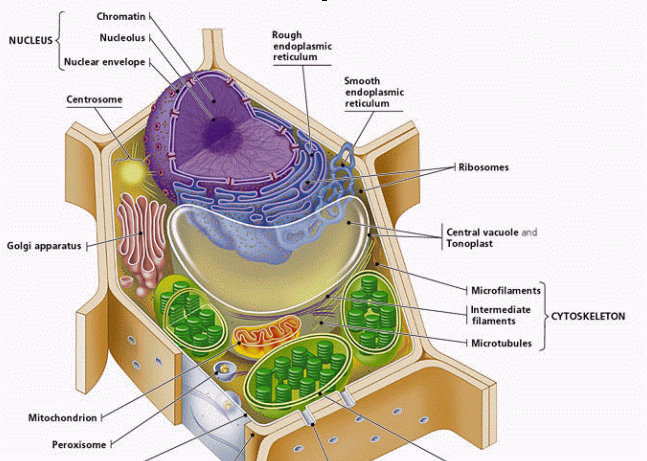
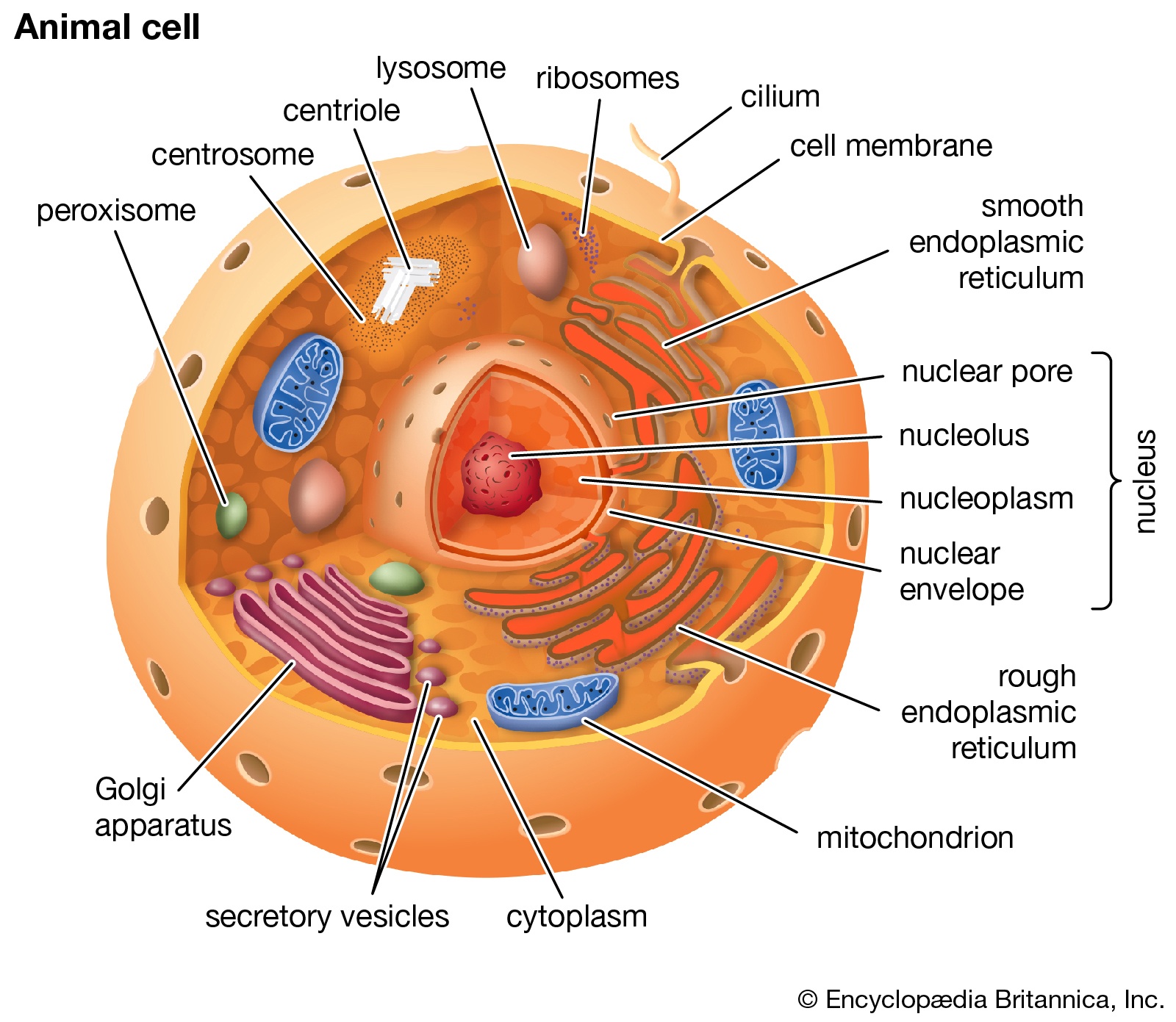
Anatomy and Physiology: Parts of a Human Cell - Visible Body The nucleus is a large organelle that contains the cell's genetic information. Most cells have only one nucleus, but some have more than one, and others—like mature red blood cells—don't have one at all. Within the nucleus is a spherical body known as the nucleolus, which contains clusters of protein, DNA, and RNA. Cellular organelles and structure (article) | Khan Academy There are two main types of cells, prokaryotic and eukaryotic. Prokaryotes are cells that do not have membrane bound nuclei, whereas eukaryotes do. The rest of our discussion will strictly be on eukaryotes. Think about what a factory needs in order to function effectively. Plasma membrane and cytoplasm (article) | Khan Academy The plasma membrane—the outer boundary of the cell—is the bag, and the cytoplasm is the goo. Of course, a cell is ever so much more than just a bag of goo. It's a complex, highly organized unit, the basic building block of all living things. And the plasma membrane and cytoplasm are actually pretty sophisticated. Cell parts and functions (article) | Khan Academy Cells contain parts called organelles. Each organelle carries out a specific function in the cell. A cell's organelles work alone and together to keep the whole cell functioning. Mitochondria are organelles that break down sugars. This process releases energy that the cell can use. The nucleus is an organelle that contains a cell's genes.
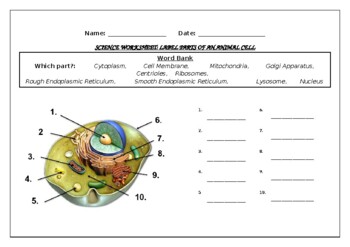
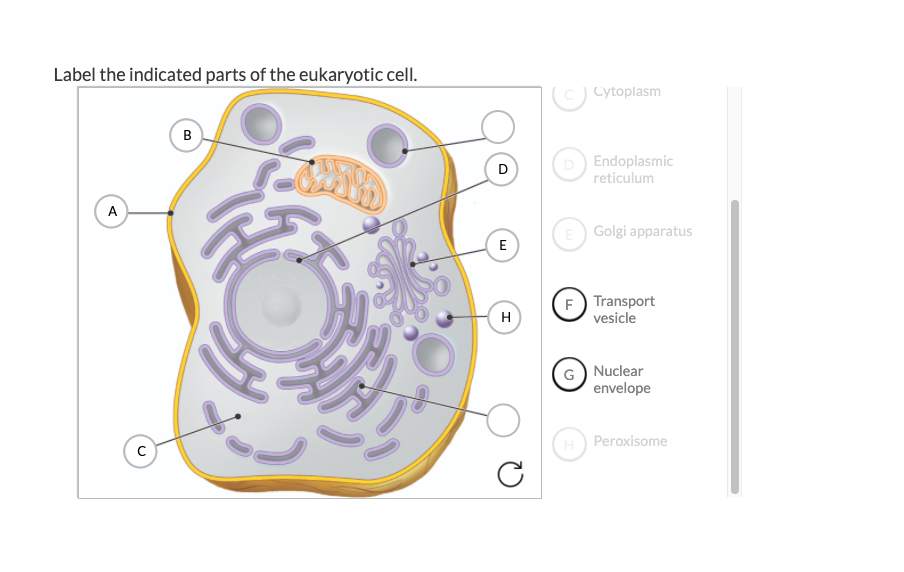
Label the cell - Teaching resources - Wordwall 10000+ results for 'label the cell'. Label the animal cell Labelled diagram. by Amargu. Label the Cell Membrane Labelled diagram. by Renatathomas. Label the Plant Cell Labelled diagram. by Armstrem. G7 Science. Label the Cell Cycle Labelled diagram. Labeling the Cell Flashcards | Quizlet Label the transmission electron micrograph of the nucleus. membrane bound organelles golgi apparatus, mitochondrion, lysosome, peroxisome, rough endoplasmic reticulum nonmembrane bound organelles ribosomes, centrosome, proteasomes cytoskeleton includes microfilaments, intermediate filaments, microtubules Identify the highlighted structures Structure of the plasma membrane (article) | Khan Academy Image modified from OpenStax Biology. The principal components of the plasma membrane are lipids (phospholipids and cholesterol), proteins, and carbohydrate groups that are attached to some of the lipids and proteins. A phospholipid is a lipid made of glycerol, two fatty acid tails, and a phosphate-linked head group. Structure of a cell | Biology library | Science | Khan Academy At the cellular level, though, some of the key differences include a cell nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, which you have (and the bacterium lacks). Here, we'll look in detail at the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Learn Cell size Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells Prokaryotic cells Intro to eukaryotic cells
Free Anatomy Quiz - The anatomy of the cell - Quiz 1 centrioles, the cytoplasm, the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulums, the golgi complex, lysosomes, microfilaments, mitochondria, the nucleolus, the nucleus, the nuclear membrane, pinocytotic vesicles, the plasma membrane, ribosomes and vacuoles. Take your knowledge of the cell further with our cell physiology quizzes : Quiz 1 --- Quiz 2
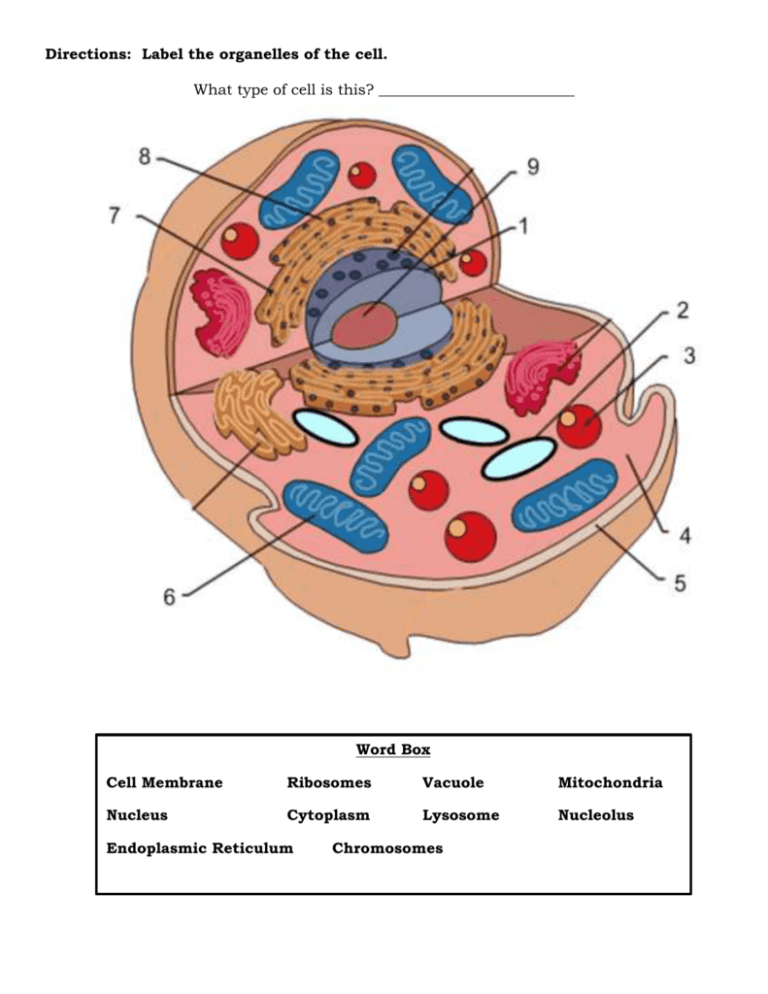



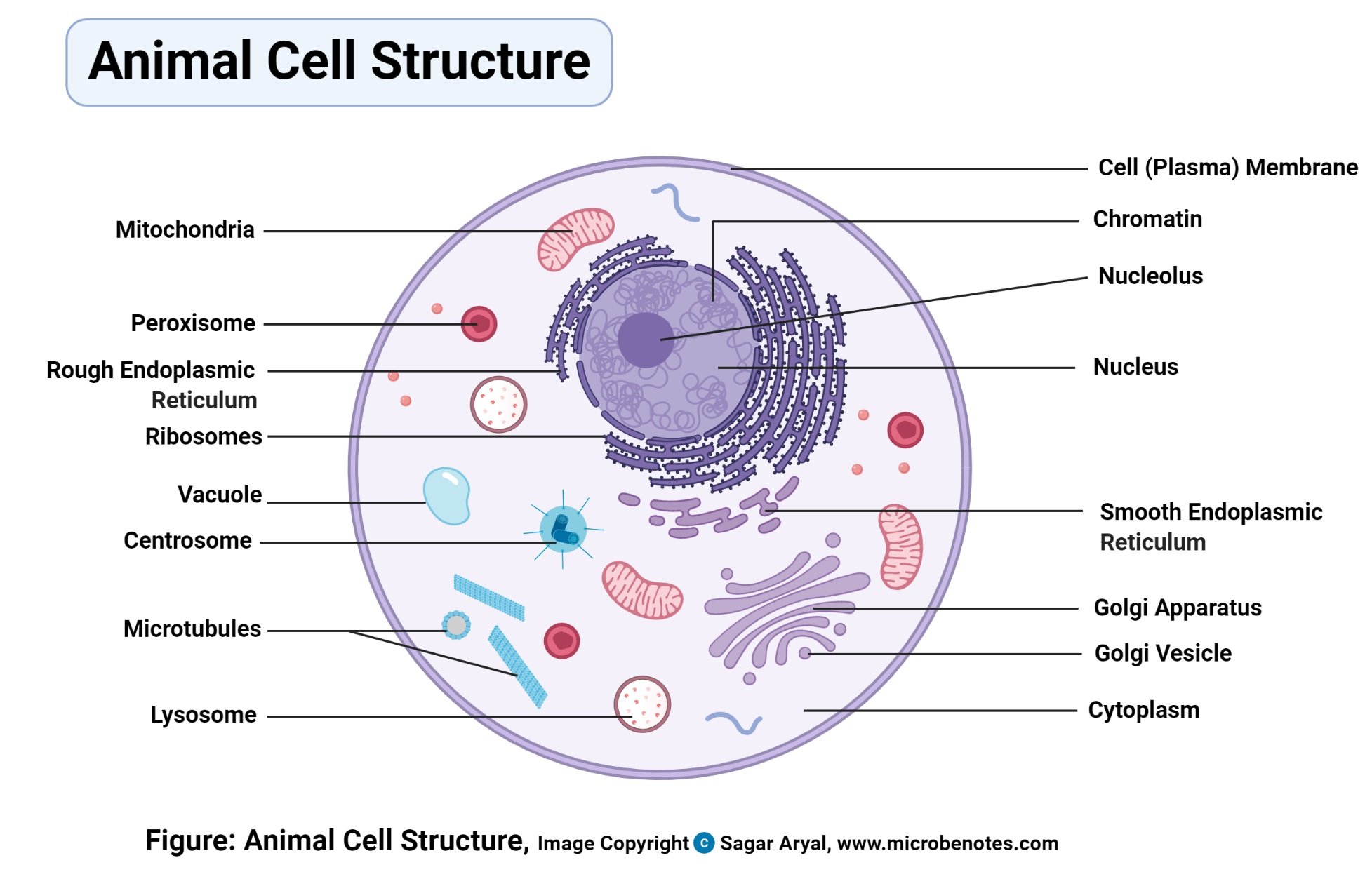

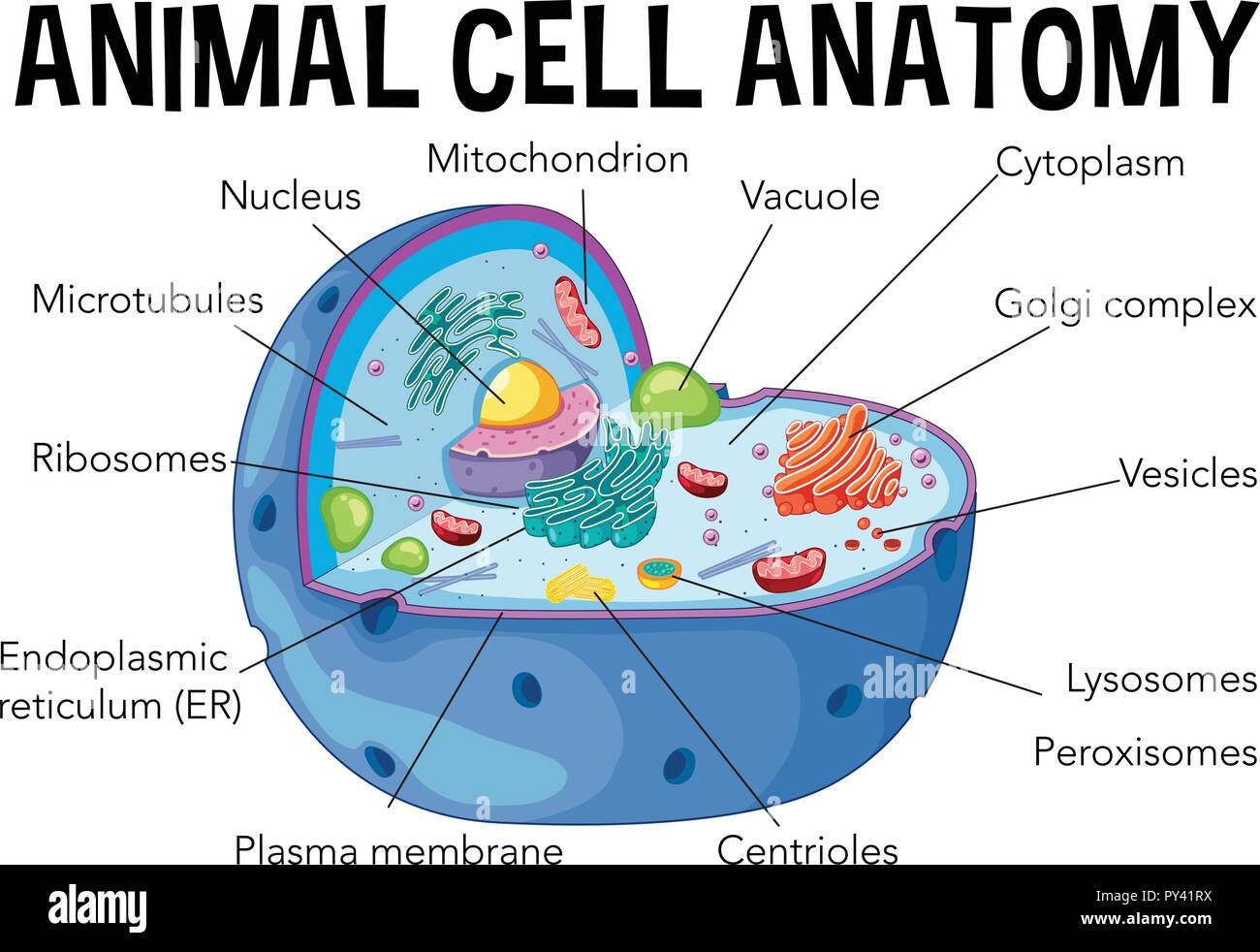
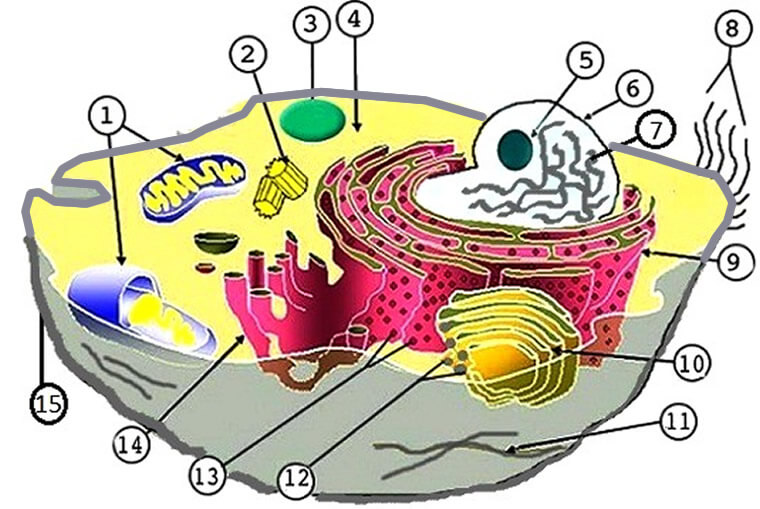
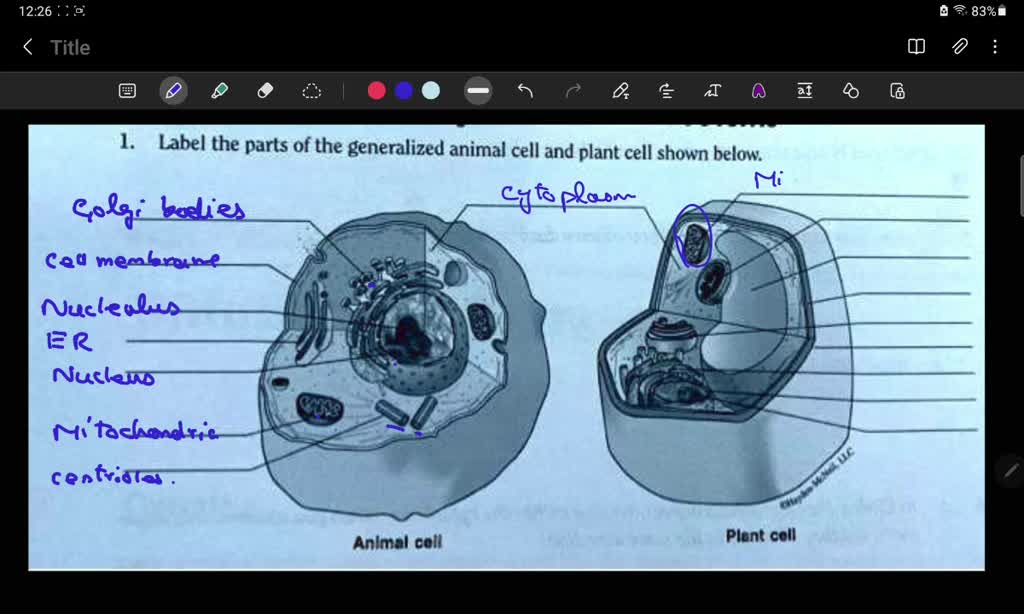
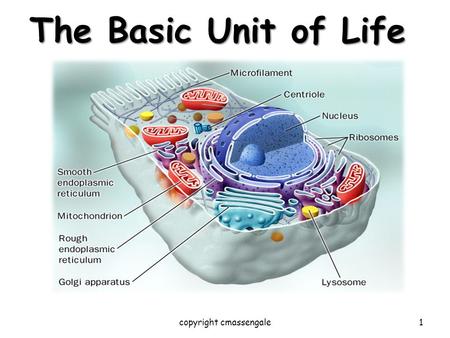


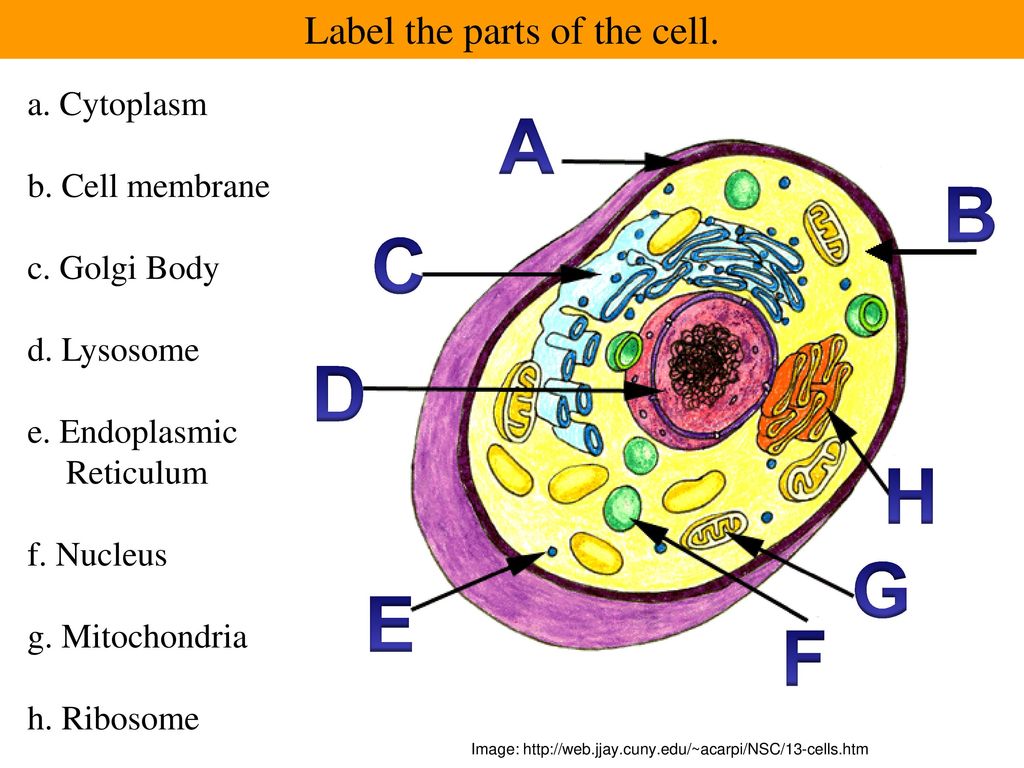
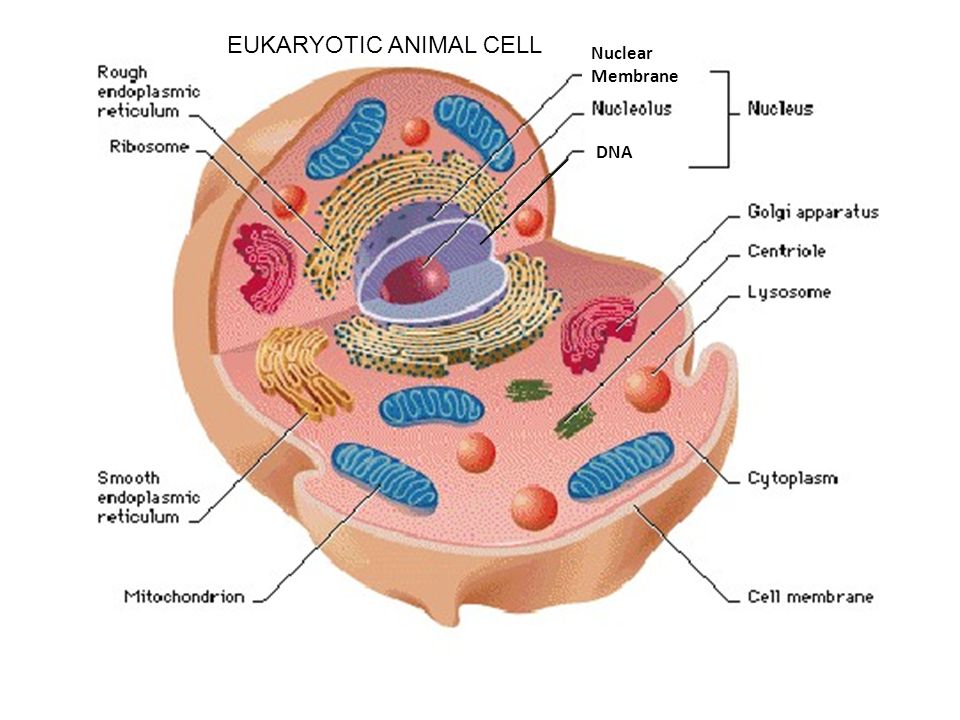

![Grade 10 biology: labeling the human cell parts] : r/HomeworkHelp](https://preview.redd.it/grade-10-biology-labeling-the-human-cell-parts-v0-arbpmln4oly91.png?auto=webp&s=20a14950158302bf8200815312a12ea0c1104fe6)
![Control & Coordination] Label the parts of a neuron in the ...](https://d1avenlh0i1xmr.cloudfront.net/03e90282-e877-422b-b0a5-8b2bb7ef2342/label-the-parts-ofa-neuron---teachoo.jpg)



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cell-membrane-373364_final-5b5f300546e0fb008271ce52.png)




Post a Comment for "41 label the parts of the cell"